Search
Brilliance™ Salmonella Agar Base
Isolate and presumptively identify Salmonella species from food samples with this chromogenic medium.
| Catalog Number | Yield |
|---|---|
| CM1092B | For 9.3L medium |
| CM1092T | For 74 L of medium |
Isolate and presumptively identify Salmonella species from food samples with chromogenic Thermo Scientific™ Brilliance™ Salmonella Agar Base (Dehydrated).
An Inhibigen compound is comprised of two components, combined together by a bond that can only be cleaved by a specific enzyme. When bound together, the inhibitor compound is not toxic and, therefore, can exist in a medium without harming micro-organisms. Once inside the cell, the bond will be cleaved if the target enzyme is present. When the bond is cleaved, the inhibitor molecule is released and disrupts cell wall synthesis, causing death of the organism. As cells die and lyse, free inhibitor is released but cannot be taken up by other cells, resulting in targeted inhibition. The Inhibigen in Brilliance Salmonella Agar targets Escherichia coli. Novobiocin and cefsulodin, presented as a freeze-dried supplement (SR0194), are added to the medium to inhibit the growth of other competing flora such as Proteus spp. and Pseudomonas spp.
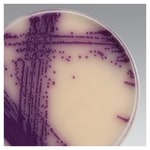
Differentiation of Salmonella from the other organisms that grow on Brilliance Salmonella Agar is achieved through the inclusion of two chromogens that also target specific enzymes: caprylate esterase and β-glucosidase. Caprylate esterase is an enzyme present in all samonellae as well as some species of Klebsiella, Enterobacter and Proteus. Organisms possessing caprylate esterase cleave the chromogen to release an insoluble purple chromophore. As the cells grow, the chromophore builds up and produces a purple-coloured colony. Some Enterobacteriaceae, including Klebsiella and Enterobacter but not Salmonella, possess β-glucosidase2. If these organisms grow, they will form blue or dark blue colonies, even if they are esterase positive, which make them easy to differentiate from purple Salmonella colonies.
Salmonella Selective Supplement, Part No. SR0194E, is also available.