Search
Citas y referencias (15)
Invitrogen™
HCS CellMask™ Stains
Easily visualize entire cells or individual cell structures during high-content screening (HCS) assays with HCS CellMask stains, which are available in a variety of colors for multiplexing flexibility and can be used immediately after fixation and permeabilization, or after antibody labeling.
| Número de catálogo | Descripción |
|---|---|
| H32714 | Tinción HCS CellMask™ Green |
| H32720 | Tinción HCS CellMask Blue |
| H32722 | Tinción cercana a IR HCS CellMask™ |
| H32713 | Tinción HCS CellMask™ Orange |
| H32712 | Tinción HCS CellMask™ Red |
| H32721 | Tinción HCS CellMask™ Deep Red |
Número de catálogo H32714
Precio (MXN)
-
Descripción:
Tinción HCS CellMask™ Green
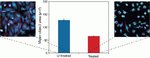
Identify entire cells (cytoplasm and nucleus) during high-content screening (HCS) assays with the versatile HCS CellMask Red, CellMask Orange, CellMask Green, CellMask Blue, CellMask Deep Red, and CellMask Near-IR stains, which are fluorophores that can be used immediately after fixation and permeabilization, or after antibody labeling. They are available in a variety of colors for multiplexing protocols.
The versatile HCS CellMask Red, CellMask Orange, CellMask Green, CellMask Blue, CellMask Deep Red, and CellMask Near-IR stains are cell delineation tools for high content screening (HCS) platforms, label the entire cell (cytoplasm and nucleus) and provide an accurate backdrop against which the features of interest can be assessed. The HCS CellMask Red and Blue stains replace the HCS CellMask Red cytoplasmic/nuclear (Cat. No. H32711) and HCS CellMask Blue cytoplasmic/nuclear stains (Cat. No. H34558), respectively.
HCS CellMask stains can be applied to cells immediately after fixation or in the last step of multiplexing protocols, and they are compatible with detergent-based cell permeabilization protocols. If only nuclear staining is desired, HCS NuclearMask stains can be used for measuring DNA content in addition to enabling robust cell demarcation. HCS NuclearMask stains are also available in a choice of colors for multiplexing flexibility.
HCS CellMask stains can be applied to cells immediately after fixation or in the last step of multiplexing protocols, and they are compatible with detergent-based cell permeabilization protocols. If only nuclear staining is desired, HCS NuclearMask stains can be used for measuring DNA content in addition to enabling robust cell demarcation. HCS NuclearMask stains are also available in a choice of colors for multiplexing flexibility.
Para uso exclusivo en investigación. No apto para uso diagnóstico o terapéutico en humanos ni en animales.
Especificaciones
ColorVerde
DescripciónTinción HCS CellMask™ Green
Método de detecciónFluorescente
EmisiónVisible
Intervalo de longitud de onda de excitación493/516
Para utilizar con (equipo)Instrumentos de alto contenido
Línea de productosCellMask
Cantidad1 juego
Condiciones de envíoTemperatura ambiente
Tipo de etiquetaColorante fluorescente
Tipo de productoTinción
SubCellular LocalizationNúcleo, citoplasma y citosol, Cytosol, Nucleus
Unit SizeEach
Contenido y almacenamiento
Incluye 1 juego de viales, que proporciona suficiente material para teñir un total de diez microplacas de 96 pocillos
Almacenar a ≤ -20 °C, disecar y proteger de la luz.
Almacenar a ≤ -20 °C, disecar y proteger de la luz.
Preguntas frecuentes
What dyes are used to make the CellMask stains?
Citations & References (15)
Citations & References
Abstract
Brown fat determination and development from muscle precursor cells by novel action of bone morphogenetic protein 6.
Journal:
PubMed ID:24658703
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) plays a pivotal role in promoting energy expenditure by the virtue of uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1) that differentiates BAT from its energy storing white adipose tissue (WAT) counterpart. The clinical implication of
Approaches to protozoan drug discovery: phenotypic screening.
Journal:
PubMed ID:23927763
Determining the activity of a compound and the potential impact on a diseased state is frequently undertaken using phenotypic or target-based approaches. Phenotypic screens have the advantage of the whole organism being exposed to the compound and thus all the targets and biological pathways associated with it. Cell penetration and
Effect of microgrooved surface topography on osteoblast maturation and protein adsorption.
Journal:
PubMed ID:25630566
Microgrooved surfaces have been used extensively to influence cell contact guidance. Guiding cell growth, extracellular matrix deposition, and mineralization is important for bone implant longevity. In this study, we investigated the osteoblast response to microgrooved metallic surfaces in serum-supplemented medium. Groove spacing was comparable with the spread osteoblast size. Focal
BMP signaling in astrocytes downregulates EGFR to modulate survival and maturation.
Journal:
PubMed ID:25330173
Astrocytes constitute a major cell population in the brain with a myriad of essential functions, yet we know remarkably little about the signaling pathways and mechanisms that direct astrocyte maturation. To explore the signals regulating astrocyte development, we prospectively purified and cultured immature postnatal rodent astrocytes. We identified fibroblast growth
Simultaneous flow cytometric analysis of IFN-? and CD4 mRNA and protein expression kinetics in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells during activation.
Journal:
PubMed ID:25123411
The application of fluorescently-labeled antibodies for flow cytometric identification and characterization of specific cell types within heterogeneous populations by their protein expression profile is well established. While detection of proteins is informative, concomitant transcript analysis in the same cells would provide a more complete and comprehensive view of intracellular signaling