Search
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
Tin(II) chloride, anhydrous, 98%
CAS: 7772-99-8 | Cl2Sn | 189.61 g/mol
化學識別
CAS7772-99-8
IUPAC Nameλ²-tin(2+) dichloride
Molecular FormulaCl2Sn
InChI KeyAXZWODMDQAVCJE-UHFFFAOYSA-L
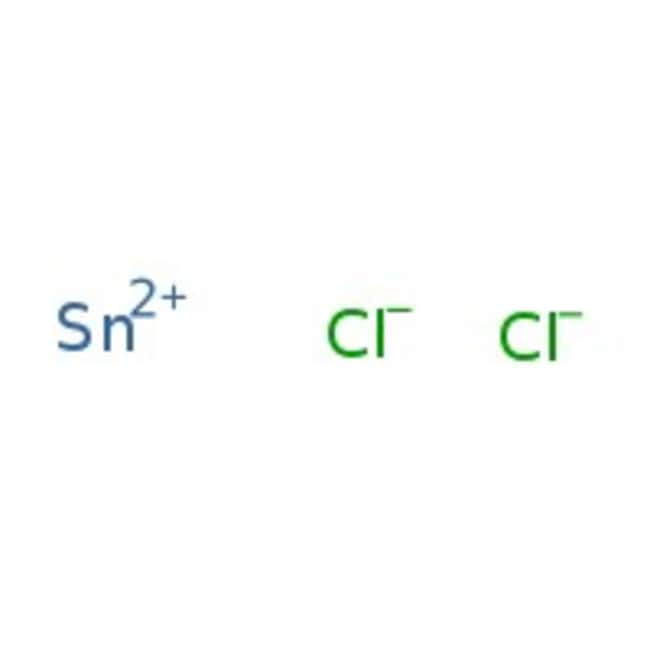
SMILES[Cl-].[Cl-].[Sn++]
檢視更多
規格 規格表
規格表
FormCrystals or powder or crystalline powder
Assay (Titration ex Chloride)≥97.5 to ≤102.5%
Appearance (Color)White
Tin(II) chloride is widely used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, for example conversion of quinones into hydroquinones, nitroaromatics into aromatic amines, and in Stephen reduction. It can be used to reduce certain metal salts into metals, tin plating, analytical testing of mercury ions, formation of silver mirrors and metal-metal bonds. It is also used for tin-plating, as a mordant in textile dyeing and as a catalyst in the production of polylactic acid. Further it is used as a food additive, wherein it serves as an anti-oxidant and a color retention agent. It can be used in the condensation of aryl aldehydes with cyclohexan-1,3-diones to synthesize xanthenes. It catalyzes direct conversion of aldehydes into beta-keto esters.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Tin(II) chloride is widely used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, for example conversion of quinones into hydroquinones, nitroaromatics into aromatic amines, and in Stephen reduction. It can be used to reduce certain metal salts into metals, tin plating, analytical testing of mercury ions, formation of silver mirrors and metal-metal bonds. It is also used for tin-plating, as a mordant in textile dyeing and as a catalyst in the production of polylactic acid. Further it is used as a food additive, wherein it serves as an anti-oxidant and a color retention agent. It can be used in the condensation of aryl aldehydes with cyclohexan-1,3-diones to synthesize xanthenes. It catalyzes direct conversion of aldehydes into beta-keto esters.
Solubility
Soluble in ethanol, acetone, ether and tetrahydrofuran. Insoluble in xylene.
Notes
Tin(II) chloride is very freely soluble in cold water. If the volume of water increases or at hot condition it hydrolyses to form an insoluble hydroxide derivative.
Tin(II) chloride is widely used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, for example conversion of quinones into hydroquinones, nitroaromatics into aromatic amines, and in Stephen reduction. It can be used to reduce certain metal salts into metals, tin plating, analytical testing of mercury ions, formation of silver mirrors and metal-metal bonds. It is also used for tin-plating, as a mordant in textile dyeing and as a catalyst in the production of polylactic acid. Further it is used as a food additive, wherein it serves as an anti-oxidant and a color retention agent. It can be used in the condensation of aryl aldehydes with cyclohexan-1,3-diones to synthesize xanthenes. It catalyzes direct conversion of aldehydes into beta-keto esters.
Solubility
Soluble in ethanol, acetone, ether and tetrahydrofuran. Insoluble in xylene.
Notes
Tin(II) chloride is very freely soluble in cold water. If the volume of water increases or at hot condition it hydrolyses to form an insoluble hydroxide derivative.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- For applications see under dihydrate.
- Karami, B.; Eskandari, K.; Zare, Z.; Gholipour, S. A New Access to 1,8-Dioxooctahydroxanthenes Using Yttrium(III) Nitrate Hexahydrate and Tin(II) Chloride Dihydrate as Effective and Reusable Catalysts. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2014, 49 (12), 1715-1722.
- Kamali, A. R. Thermokinetic characterisation of tin(II) chloride. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 118 (1), 99-104.
- Chia, S. -P.; Li, Y.; Ganguly, R.; So, C. -W. Heteroleptic Germanium(II) and Tin(II) Chlorides Supported by Anionic Ligands Derived from 2,3-Dimethyl-1,4-diaza-1,3-butadiene. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 526-532.