Search
Bioss
ATG9B Polyclonal Antibody
{{$productOrderCtrl.translations['antibody.pdp.commerceCard.promotion.promotions']}}
{{$productOrderCtrl.translations['antibody.pdp.commerceCard.promotion.viewpromo']}}
{{$productOrderCtrl.translations['antibody.pdp.commerceCard.promotion.promocode']}}: {{promo.promoCode}} {{promo.promoTitle}} {{promo.promoDescription}}. {{$productOrderCtrl.translations['antibody.pdp.commerceCard.promotion.learnmore']}}
Product Details
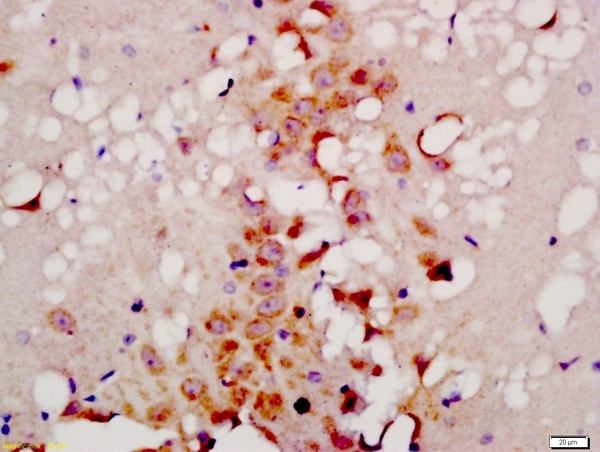
BS-4011R
Species Reactivity
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Immunogen
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
Target Information
Autophagy, the process of bulk degradation of cellular proteins through an autophagosomic-lysosomal pathway is important for normal growth control and may be defective in tumor cells. It is involved in the preservation of cellular nutrients under starvation conditions as well as the normal turnover of cytosolic components. This process is negatively regulated by TOR (Target of rapamycin) through phosphorylation of autophagy protein APG1. ATG9B plays a role in autophagy and it's highly expressed in placenta and pituitary gland.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
References (0)
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: APG9-like 2; ATG9; ATG9 autophagy related 9 homolog B; autophagy 9-like 2 protein; Autophagy-related protein 9B; endothelial nitric oxide synthase antisense; nitric oxide synthase 3 antisense; Nitric oxide synthase 3-overlapping antisense gene protein; Protein sONE
Gene Aliases: Apg912; APG9L2; Apgdc2; ATG9B; eONE; Gm574; NOS3AS; RGD1560887; SONE
UniProt ID: (Human) Q674R7, (Mouse) Q6EBV9
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 285973, (Rat) 499973, (Mouse) 213948

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support