Tracking the spread and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 is important to help address the global crisis. As the virus transfers from host to host, it evolves across individuals and can acquire mutations that make it more virulent, enabling it to potentially affect more individuals. This evolutionary arms race across the globe with a multitude of strains makes it essential for researchers to quickly establish potential treatment and possible preventative measures to combat and halt the virus from continually evolving and affecting more people. Due to the genetic differentiation across strains geographically, viral surveillance and epidemiological research allows us to better understand the virus and its spread, but a major challenge for researchers when exploring a cure is tracking and monitoring the evolutionary differences across viral strains as it rapidly evolves during transmission. Tracking the virus allows us to identify its source, develop future treatments based on how it evolves, and put appropriate potential preventative measures in place to limit its distribution.
Next generation sequencing (NGS) is a tool that allows for rapid sequencing of thousands of genetic mutations across samples in parallel. The high throughput nature of NGS allows researchers to look at the entire SARS-CoV-2 genome across many samples at a time to get a more complete picture.
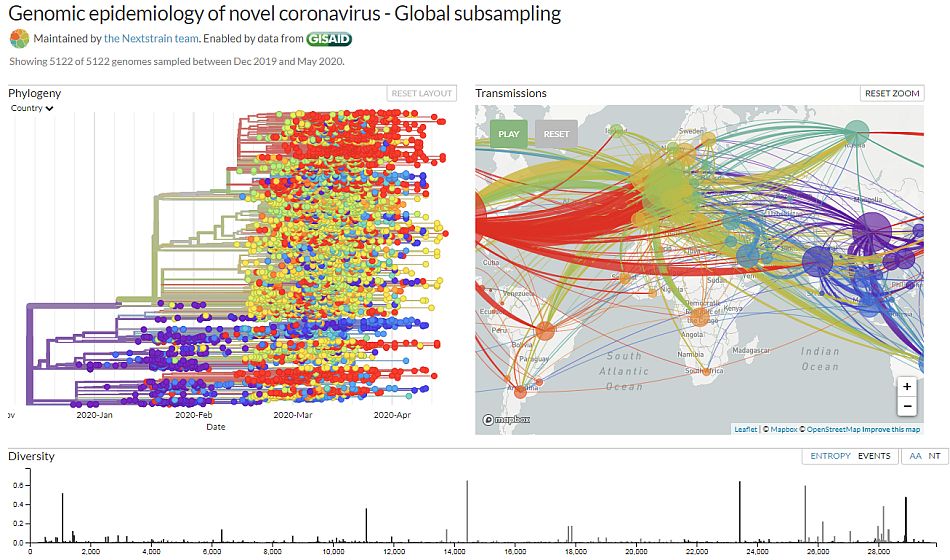
Nextstrain.org is an open source resource that utilizes public NGS repositories to decipher metadata and rapidly monitor various viral strains in close to real time. Not only is the spread of the virus tracked geographically, but also on an evolutionary basis over time via a phylogenetic tree. In regard to SARS-CoV-2, this allows for policy makers and the public to get information prior to publication—when it could be too late to understand—or implement laws to impact the rate of viral evolution and spread. However to accurately depict the evolution in real time, there is a necessity for rapid targeted sequencing that is user-friendly and robust enough to differentiate across various strains, given how quickly the virus spreads.
![]()
Genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 from nextstrain.org, data from
December 2019 through May 2020
Researchers contributing to the data that is now available on nextstrain.org have simplified their research by leveraging the latest sequencing solution from leading Ion Torrent technology for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance, epidemiology and contact tracing and tracking. The Ion AmpliSeq SARS-CoV-2 Research Panel is part of an automated sample-to-answer workflow that includes the assay and easy-to-use analysis plugin package, a powerful yet user-friendly analysis solution enabling researchers to focus on the biological meaning of their data. The kit consists of 2 primer panels to give complete viral genome sequencing and variant detection in samples that contain as low as 20 viral copies. Its ability to robustly and accurately detect variants of rapid mutation in less than a day could provide crucial data for policy makers to make better informed decisions and for researchers to gather more discrete information for vaccine research.
Learn more about rapid, automated and accurate targeted NGS for SARS-CoV-2 epidemiological research
Explore Ion Torrent targeted NGS solutions for SARS-CoV-2 research
Reference:
[1] “Genomic epidemiology of novel coronavirus – Global subsampling” by nextstrain.org is licensed under CC-BY-4.0.