In the rapidly advancing field of medical diagnostics, liquid biopsy stands out as an innovative technique that is advancing the way we detect and monitor diseases. Unlike traditional biopsies, which require invasive procedures to extract tissue samples, liquid biopsy offers a minimally invasive alternative by isolating cells from complex samples such as blood. This approach not only lowers the impact of sample collection but also allows for a wealth of information that can be crucial for early disease research, treatment research, and personalized medicine research.
The importance of isolating cells from blood and other complex samples cannot be overstated. Blood contains a diverse array of cells, including circulating tumor cells (CTCs), immune cells, and other rare cell types that can provide valuable insights into research on a patient’s health status. By effectively isolating these cells, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms.
Magnetic cell separation
Magnetic cell separation is a technique used to isolate specific cell types from a heterogeneous population based on the presence of specific surface markers. This method involves magnetic beads conjugated with antibodies binding to the target cells. After a short incubation, the bead-bound cells can be isolated from the sample using a magnet. This method allows for the rapid and gentle isolation of cells for downstream applications, such as flow cytometry, cell culture, or molecular analysis. Cell isolation for your research can be labor-intensive and time-consuming, often requiring multiple steps and manual handling, which can introduce variability and reduce reproducibility. At the core of addressing these challenges are Dynabeads™ magnetic beads. For the past four decades, Dynabeads magnetic beads have led advancements in cell isolation technology. These superparamagnetic beads are distinguished by their consistent physical and chemical properties, including uniformity and monodispersity, making them essential for a wide range of applications. Dynabeads magnetic beads enable high-performance, gentle isolation of immune cells and other cell types. They can facilitate the isolation of viable cells from a variety of species with the cell isolation method that best suits your research needs.
With advancements in automated cell isolation techniques, the integration of Dynabeads magnetic beads technology into KingFisher™ Automation systems has significantly enhanced the efficiency of the cell isolation process for researchers. Automation reduces the need for manual handling, increases reproducibility by avoiding operator variability and increases throughput, making cell isolation for research more reliable and scalable.
In this blog, we will delve into magnetic bead-based cell isolation, exploring the step-by-step automation techniques that streamline and enhance the efficiency of this important research procedure. We will also share practical tips on how to optimize your cell isolation script, helping ensure that you achieve the highest possible yield and purity of isolated cells for your research. Whether you are a researcher, or simply interested in the latest advancements, this blog will help provide you with a valuable overview of automated cell isolation.
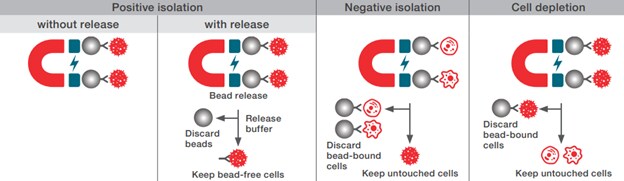
Comparing positive cell isolation, negative cell isolation, and cell depletion
Several methods exist for cell isolation, each offering different advantages and tailored applications. Among these, Dynabeads magnetic beads are recognized for their efficiency and specificity in research applications. Let’s delve into the different cell isolation methods using Dynabeads magnetic beads and understand their benefits.
Positive isolation without release
Positive isolation without release can be performed using magnetic beads coated with a specific antibody for the isolation of all cells expressing the corresponding cell surface molecule. The bead-bound cells are isolated from the sample using a magnet and are then available for downstream molecular research applications. Read more.
Positive isolation with release
Positive isolation with release can be performed using magnetic beads coated with a specific antibody for the isolation of all cells expressing the corresponding cell surface molecule. The bead-bound cells are isolated from the sample using a magnet. Then, the cells are released from the magnetic beads using a release buffer. The beads are removed using a magnet, and the bead-free cells are available for any downstream application. Read more.
Negative Isolation
Negative Isolation is depletion of unwanted cell types from the sample, leaving the target cells untouched and free of antibodies and beads. An antibody mix targeting the unwanted cells is first added to the sample, followed by addition of magnetic beads that are specific for the labeling antibodies. The bead-cell complexes are removed using a magnet, leaving the pure and untouched cells of interest in the supernatant for research applications. Read more.
Cell depletion
Cell depletion can be performed using magnetic beads conjugated with a specific antibody for depletion of all cells expressing the corresponding cell surface molecule. The bead-bound cells are removed from the sample using a magnet. The depleted sample is less complex and enriched for the cells of research interest (e.g. CTCs). Read more.
Note: consider adding drop down tables for Cell Type Targeted and Cell Surface Marker from dynabeads pages. Other option to just have featured products and include KingFisher and Dynabeads.
Automated cell isolation
Automated cell isolation for research can be achieved using protocols for the rapid and efficient isolation of various immune cell types on KingFisher instruments. These protocols offer quick methods for isolating immune cells such as T cell subsets (CD3, CD4, CD8), B cells (CD19), monocytes (CD14) or all lymphocytes (CD45). Additionally, these automated protocols can serve as a foundation for isolating other cell types, providing a versatile tool for immunological research. In the following sections, we will demonstrate how KingFisher instruments can simplify and accelerate the cell isolation processes for your research.
Steps to automate cell isolation
Step 1: Sample Preparation
- Cells are sensitive to sampling, handling, storage conditions and -time. The accuracy and reliability of cell isolation depends on the quality of the biological sample (e.g. blood or tissue). Follow specific protocols to prepare the samples appropriately.
Step 2: Magnetic bead selection
- Select the appropriate Dynabeads magnetic beads and isolation method (positive isolation, negative isolation, or cell depletion) according to the sample, target cell and downstream research application.
Step 3: Setting Up the KingFisher Instrument
- Plate loading: Place your prepared samples, magnetic beads and buffers into the designated wells of the KingFisher plates, following the protocol layout.
Step 4: Running the Automated Protocol
- Select Protocol: Choose the pre-programmed script on the KingFisher instrument that corresponds to your isolation method.
- Start Run: Initiate the automated process. The KingFisher instrument will carry out the cell isolation procedures for research, including binding, washing, and release steps, with minimal manual intervention.
Step 5: Collection of Isolated Cells
- Positive isolation without release: Isolated, bead-bound cells can be collected in the bead-fraction.
- Positive isolation with release: Isolated, bead-free cells can be collected separately from the bead fraction.
- Negative isolation: Isolated, bead-free cells can be collected separately from the bead fraction.
- Cell depletion: The depleted sample can be collected separately from the bead fraction.
Step 6: Analysis
- Proceed with downstream applications such as cell culture, flow cytometry, protein or nucleic acid extraction and analysis.
Tips and tricks for automating cell isolation
Optimizing automated cell isolation involves several important parameters:
- Incubation time
- Incubation temperature
- Mixing conditions during incubation
- Efficiency of bead capture on the magnet
Incubation Time for efficient positive isolation
To determine the optimal incubation time for efficient positive isolation in this research study, CD3 positive Jurkat cells were used as the starting material to eliminate potential blood donor variations. The Jurkat cells were incubated with Dynabeads magnetic beads for 10 – 60 minutes. Isolation efficiency was assessed by flow cytometric analysis, measuring the remaining cells in the depleted fraction. Research results indicated that isolation efficiency using KingFisher instruments was comparable to manual isolation. Notably, most binding occurred within the first 10 minutes, and extending the incubation time from 30 to 60 minutes did not increase yield. Prolonged incubation time will generally increase non-specific binding.

Incubation Temperature for cell capture
Using the KingFisher Apex or Duo Prime instruments, the cell capture can be performed under cooling conditions. Performing cell isolation at lower temperatures will slow down the biological activity of the cells and reduce non-specific binding but may reduce cell isolation efficiency. This can be beneficial when downstream research applications require unchanged cells of high purity.
Mixing during cell isolation
Optimal mixing conditions during cell isolation helps ensure high yield, high purity and optimal viability of target cells for your research. Three different mixing conditions were tested on KingFisher instruments during cell isolation: “Slow”, “Medium,” and “Fast.” “Medium” and “Fast” mixing resulted in significant cell loss, and remaining cells showed reduced viability. “Slow” mixing during cell isolation demonstrated equal isolation efficiency and viability as compared to manual isolation. Therefore, gentle mixing during isolation is recommended to achieve high yield, purity and viability of isolated cells.

Bead Capture After Cell Isolation
To maximize cell isolation or depletion efficiency for your research, it is essential to capture all bead-bound cells in the magnetic separation step. We compared magnetic separation involving one (1x), two (2x) and three (3x) cycles of bead capture. Introducing two cycles of bead capture in the automated protocol resulted in equal or better cell isolation efficiency as compared to manual cell isolation.

Advantages of Automating cell isolation with KingFisher Instruments
KingFisher instruments, the KingFisher Flex, Duo Prime, and Apex systems, automate the cell isolation process for researchers, reducing hands-on time and increasing consistency. These instruments utilize Dynabeads magnetic beads for gentle and efficient cell isolation without the need for centrifugation or columns.
The automation of cell isolation using KingFisher instruments together with Dynabeads magnetic beads represents a significant advancement in the field of cellular analysis and liquid biopsy research. By offering a fast, efficient, and reproducible solution, these instruments are poised to accelerate research.
Related articles and resources
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
© 2025 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. All trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries unless otherwise specified.