HIDS Rome, held this last May, was a treasure trove of information from labs around the world, discussing their implementation of mitochondrial DNA analysis. These labs are applying mtDNA analysis in criminal casework, missing persons, and ancient DNA applications.
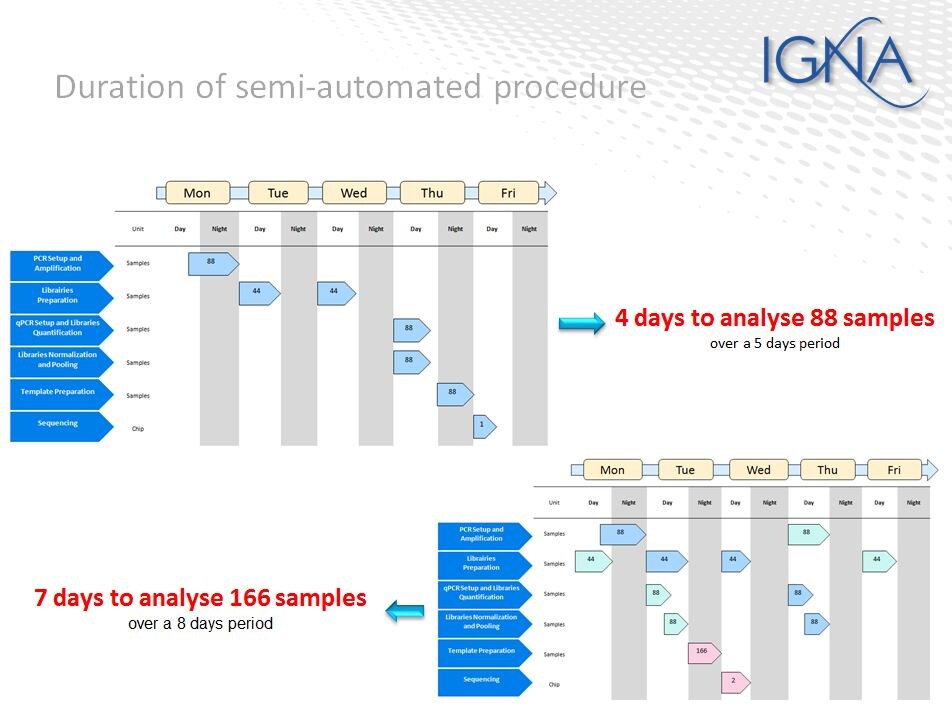
IGNA (Nantes, France) is an early user of NGS in forensic applications and they have developed procedures for using SNPs in cases where there is no match to DNA databases. Recently they had the need to screen 400 hair samples and they chose to use the Applied Biosystems Precision ID mtDNA Control Region Panel for this project. To best meet the lab’s need, they embarked on an automation project with Hamilton Bonaduz AG and Thermo Fisher Scientific to automate library preparation on the Hamilton ID NGS-T STARlet workstation. Frank Jaffredo outlined their testing procedures and noted they were able to reduce the total time and provide full traceability while maintaining flexibility in the number of libraries prepared each time (1-88). Their validation is in process for mtDNA, SNP and STR library preparations.
The California Department of Justice administers the Missing Persons DNA Program which assists law enforcement with the identification of unknown remains. They have begun an internal validation of the Applied Biosystems Precision ID mtDNA Whole Genome Panel to assist their identification efforts. Daniela Cuenca described validation results and the analysis of missing persons’ non-probative samples. Of the 22 non- probative casework samples, 45% provided results using Sanger sequencing (targeting HVI and HVII) while 85% generated results from NGS analysis.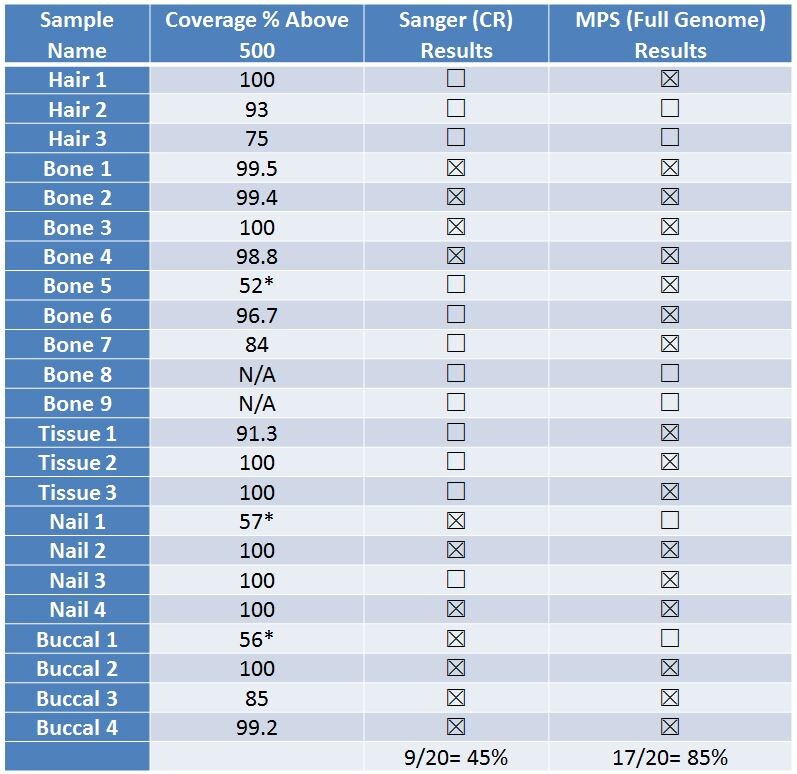
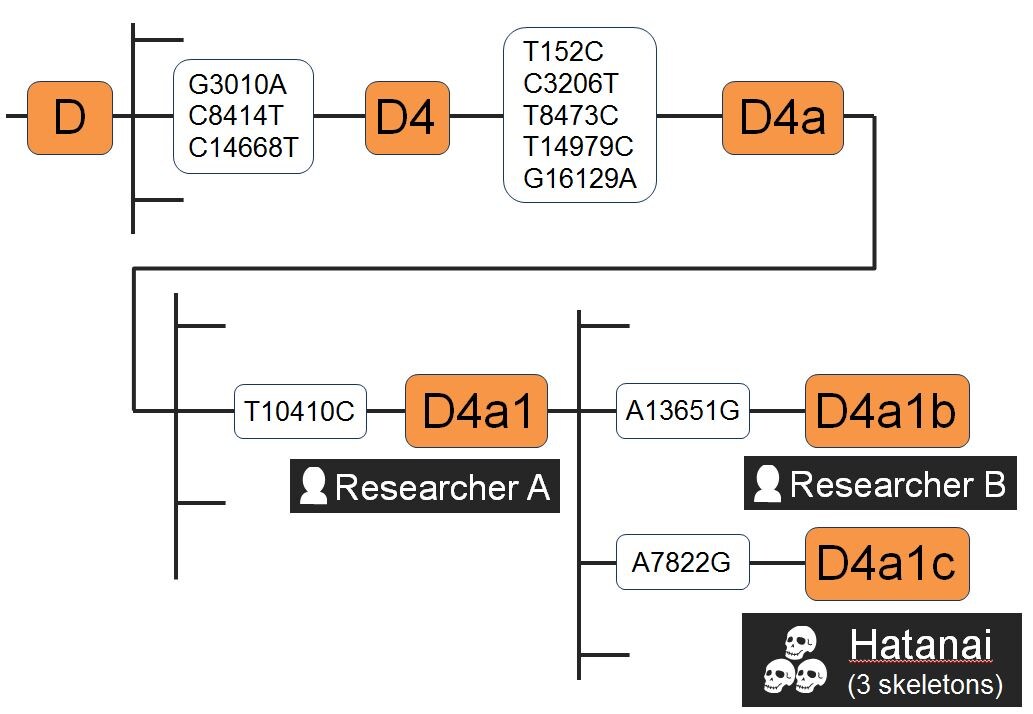
Masaki Hashiyada from Kansai Medical University outlined a project in his lab that has used the Precision ID mtDNA Whole Genome Panel as well. They have unknown remains from 3 cemeteries in the Hatanai archaeological site and these remains could be 300 years old.In a previous study, they had found that ~ 36% of Japanese population typed as haplogroup D4. In this study, they found that all 3 remains typed at D4a1c. To ensure there was no contamination from the researchers, they were also typed. The lab concluded that sequencing of the Control Region only would not have discriminated between the individuals, only the Whole Genome was able to accomplish that level of haplogroup determination.
These recent advances in next-generation sequencing now makes it possible to sequence the mtGenome, which increases discrimination and sensitivity. But analysis of the mtGenome is challenging – alignments can be misleading and may result in incorrect variant calls, and contamination from nuclear DNA from small samples may obscure true variants. Applied Biosystems Converge software NGS analysis module now contains parameters for analyzing the both the Precision ID mtDNA Whole Genome Panel and the Precision ID mtDNA Control Region Panel. This new mito variant caller integrates various sources of knowledge about mtDNA, including phylotree, EMPOP and NUMTs statistics, that avoids many of the pitfalls of standard algorithms. This knowledge is integrated into the alignment algorithm itself to distinguish true variant calls from NUMT contamination and sequencing artefacts. It also provides haplotype and haplogroup information, along with point and length heterplasmies. This automated analysis pipeline provides a fast time to result for these challenging samples.
For Research Forensic or Paternity Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.




Interesată