Search
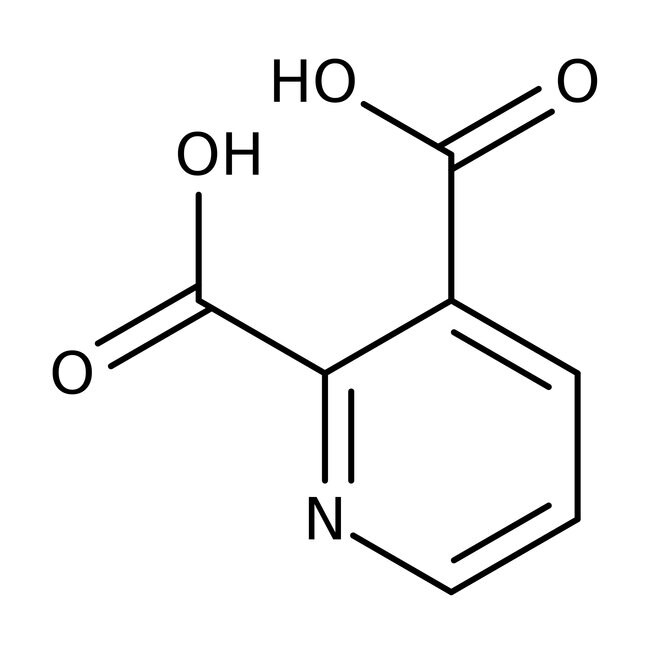
Pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid, 99%
Quinolinic acid is an endogenous NMDA agonist. Quinolinic acid is a metabolite of tryptophan that acts as a putative NMDA receptor agonist. Quinolinic acid is an excitotoxic metabolite and an agonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. properties of KYNA raise the possibility of a functional link between KYNA and QUIN in the brain which may be of relevance for an understanding of human neurodegenerative disorders. Quinolinic acid is a potent endogenous excitant at amino acid receptors in CNS.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Quinolinic acid is an endogenous NMDA agonist. Quinolinic acid is a metabolite of tryptophan that acts as a putative NMDA receptor agonist. Quinolinic acid is an “excitotoxic” metabolite and an agonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. properties of KYNA raise the possibility of a functional link between KYNA and QUIN in the brain which may be of relevance for an understanding of human neurodegenerative disorders. Quinolinic acid is a potent endogenous excitant at amino acid receptors in CNS.
Solubility
Soluble in water (partly), alkalies, dilute aqueous base, DMSO, and alcohol (slightly).
Notes
Store in cool place. Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Store away from strong oxidizing agents.
General References:
- MF Beal,; RJ Ferrante,; KJ Swartz,; NW Kowall. Chronic quinolinic acid lesions in rats closely resemble Huntington's disease. The Journal of Neuroscience,. 1991, 11(6), 1649-1659.
- Dr Melvyn P. Heyes PhD,; Bruce J. Brew MD,; Alex Martin PhD,; Richard W. Price MD,; Andres M. Salazar MD.Quinolinic acid in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in HIV-1 Infection: Relationship to clinical and neurological status. Annals of Neurology. 1991 , 29 (2),202-209.