Search
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
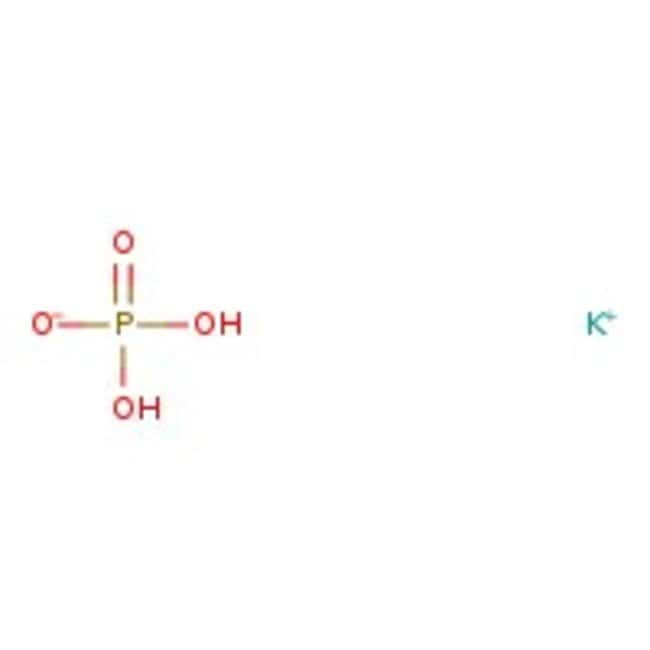
Potassium phosphate, 0.2M buffer soln., pH 7.4
CAS: 7778-77-0 | H2KO4P | 136.08 g/mol
Catalog number J62397.K2
also known as J62397-K2
Price (JPY)Request A Quote
-
Quantity:
1 L
Chemical Identifiers
CAS7778-77-0
IUPAC Namepotassium dihydrogen phosphate
Molecular FormulaH2KO4P
InChI KeyGNSKLFRGEWLPPA-UHFFFAOYSA-M
SMILES[K+].OP(O)([O-])=O
View more
Specifications Specification Sheet
Specification Sheet
Appearance (Color)Clear colorless
ConcentrationPotassium Phosphate Monobasic/Potassium Phosphate Dibasic: 200 mM
pH7.2-7.6
FormLiquid
Potassium phosphate buffer is typically used as a component for a wide variety of media used in the culture of microorganisms, as a component in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). In addition to helping maintain pH, it supplies essential phosphate.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Potassium phosphate buffer is typically used as a component for a wide variety of media used in the culture of microorganisms, as a component in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). In addition to helping maintain pH, it supplies essential phosphate.
Solubility
Soluble in water, Insoluble to slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in alcohol.
Notes
Store sealed bottle containing the dehydrated medium at 2 - 30C. Once opened and recapped, place container in a low humidity environment at the same storage temperature. Protect from moisture and light by keeping container tightly closed.
Potassium phosphate buffer is typically used as a component for a wide variety of media used in the culture of microorganisms, as a component in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). In addition to helping maintain pH, it supplies essential phosphate.
Solubility
Soluble in water, Insoluble to slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in alcohol.
Notes
Store sealed bottle containing the dehydrated medium at 2 - 30C. Once opened and recapped, place container in a low humidity environment at the same storage temperature. Protect from moisture and light by keeping container tightly closed.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Pardue, K., and Williams, D. Quantitative determination of non-ionic surfactants in protein samples, using ion-exchange guard columns. . Biotechniques. 1993, 14(4), 580-583.
- Pikal-Cleland, K.A., et al. Protein denaturation during freezing and thawing in phosphate buffer systems: monobasic and tetrameric beta-galactosidase. . Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 384(2), 398-406.