Search
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
Cerium(IV) ammonium nitrate, 98+%
Cerium(IV) ammonium nitrate, >-98%, H8CeN8O18, CAS Number-16774-21-3, Ammonium cerium(IV) nitrate; CAN, 1000g, Transport Hazard Class: 5.1; Packing Group: II; Proper Shipping Name: NITRATES, INORGANIC, N.O.S., 240-827-6, 548.23, H272-H290-H302-H314-H317-H335 | CAS: 16774-21-3 | H8CeN8O18
化学物質識別子
CAS16774-21-3
IUPAC Nameλ⁴-cerium(4+) bis(nitric acid) diamine tetranitrate
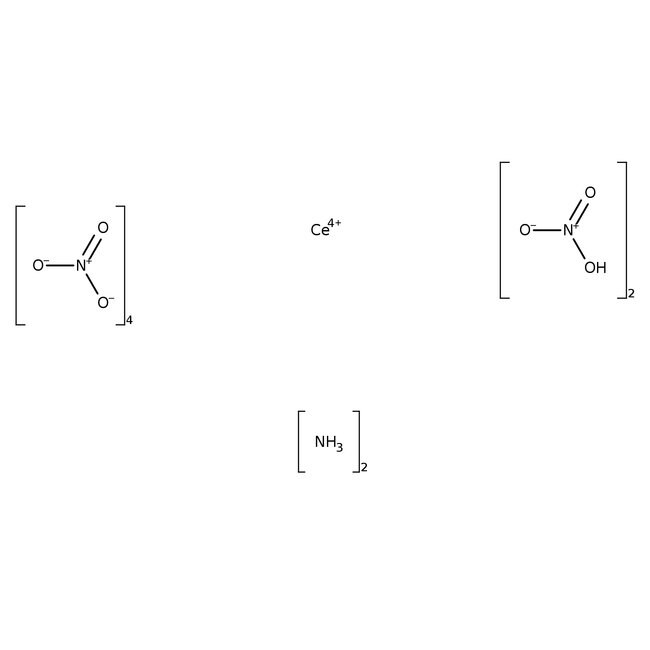
Molecular FormulaCeH8N8O18
InChI KeyWIBGOERAEYJBOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SMILESN.N.[Ce+4].O[N+]([O-])=O.O[N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O
さらに表示
仕様 スペックシート
スペックシート
Assay (unspecified)>98.0%
FormCrystals or Crystalline powder
Residual water≤2.0%
Appearance (Color)Orange
Total rare earth oxidesca 30.0%
Cerium(IV) ammonium nitrate is widely utilized as an oxidant for many functional groups like alcohols, phenols and ethers as well as C-H bonds. It acts as a deprotection reagent for alcohol in organic synthesis. It is useful in the synthesis of heterocycles like quinoxaline derivatives which is used in dyes, organic semiconductors and DNA cleaving agents. It is an active component of chrome etchant, which is used in the production of photomasks and liquid crystal displays.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Cerium(IV) ammonium nitrate is widely utilized as an oxidant for many functional groups like alcohols, phenols and ethers as well as C-H bonds. It acts as a deprotection reagent for alcohol in organic synthesis. It is useful in the synthesis of heterocycles like quinoxaline derivatives which is used in dyes, organic semiconductors and DNA cleaving agents. It is an active component of chrome etchant, which is used in the production of photomasks and liquid crystal displays.
Solubility
Soluble in water and alcohol.
Notes
Store in cool place. Hygroscopic. Incompatible with strong reducing agents and powdered metals.
Cerium(IV) ammonium nitrate is widely utilized as an oxidant for many functional groups like alcohols, phenols and ethers as well as C-H bonds. It acts as a deprotection reagent for alcohol in organic synthesis. It is useful in the synthesis of heterocycles like quinoxaline derivatives which is used in dyes, organic semiconductors and DNA cleaving agents. It is an active component of chrome etchant, which is used in the production of photomasks and liquid crystal displays.
Solubility
Soluble in water and alcohol.
Notes
Store in cool place. Hygroscopic. Incompatible with strong reducing agents and powdered metals.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Versatile oxidizing agent. For reviews, see: Chem. Rev., 92, 29 (1992); J. Prakt. Chem./ Chem. Ztg., 336, 470 (1994); Synlett, 834 (1999); 3014 (2005); Acc. Chem. Res., 37, 21 (2004). Examples of oxidations with CAN:
- Selective conversion of alcohols to aldehydes: J. Chem. Soc., 5777 (1965); J. Org. Chem., 32, 2349, 3865 (1967). Oxidation of benzylic methyl groups to aldehydes or acetates: J. Org. Chem., 31, 2033 (1966); 45, 3906 (1980). For selective oxidation of 2-methylpyrroles to the aldehydes, see: Tetrahedron Lett., 36, 4345 (1995). Phenols to quinones: Synthesis, 347 (1973); Liebigs Ann. Chem., 1655, 1669 (1986). Cleavage of vic-diols to ketones and ɑ-hydroxy ketones to acids: J. Org. Chem., 34, 869 (1969); Synthesis, 560 (1972). Conversion of ɑ-diketones and á-keto esters to carboxylic acids: J. Org. Chem., 71, 4516 (2006). Oxidative bisdecarboxylation of malonic acid derivatives: Tetrahedron Lett., 29, 769 (1988). Regeneration of carbonyl compounds from oximes or semicarbazones: Can. J. Chem., 47, 145 (1969); Synthesis, 347 (1973). Catalytic deprotection of Boc protected alcohols, amines and thiols: Tetrahedron Lett., 37, 2035 (1996). Debenzylation of N-benzyl tertiary amines: J. Chem. Soc., Perkin 1, 3765 (2000). Decomplexation of transition metal π-complexes: Org. Synth. Coll., 8, 460 (1993). Oxidative addition of olefins to the ɑ-position of ketones: Tetrahedron Lett., 28, 5357 (1987); Synth. Commun., 18, 1841 (1988).
- For formation of dithioacetals, see 1,2-Ethanedithiol, L12865. For cleavage of dithioacetals, see 1,3-Dithiane, A10505.
- Catalyst for mild, selective opening of epoxides: Tetrahedron, 47, 9861 (1991).
- The direct conversion of aldehydes to nitriles in aqueous NH3, under extremely mild conditions, is mediated by CAN: Synlett, 262 (2003).