Search
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
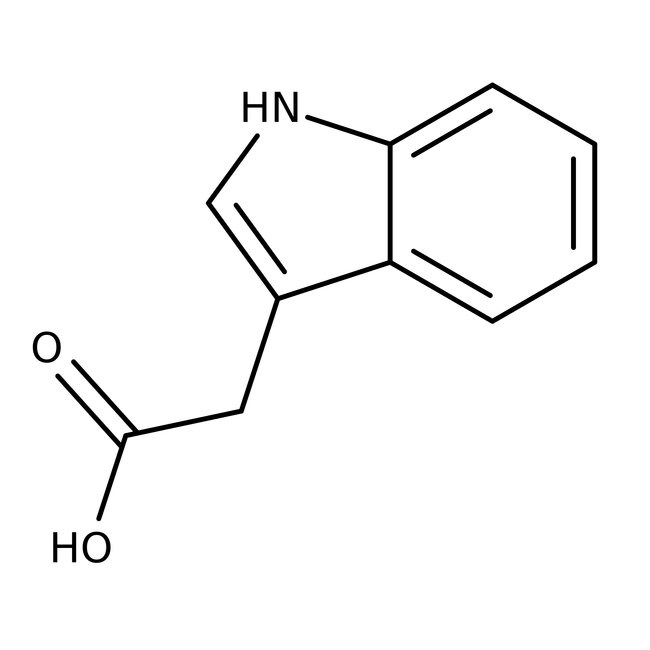
1H-Indole-3-acetic acid, 98%
1H-Indole-3-acetic acid, CAS # 87-51-4, also known as indole-3-acetic acid, is a monocarboxylic acid mainly used as a plant growth hormone and is the most common naturally occurring plant hormone of the auxin family. | CAS: 87-51-4 | C10H9NO2 | 175.19 g/mol
化学物質識別子
CAS87-51-4
IUPAC Name2-(1H-indol-3-yl)acetic acid
Molecular FormulaC10H9NO2
InChI KeySEOVTRFCIGRIMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SMILESOC(=O)CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C12
さらに表示
仕様 スペックシート
スペックシート
Appearance (Color)White to yellow to beige to light brown
Appearance (Form)Powder or crystals
Infrared spectrumConforms
Melting point165°C to 169°C
HPLC>=97.5 %
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Acros Organics product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Acros Organics product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
General Information
• 1H-Indole-3-acetic acid is a plant growth hormone that belongs to the auxin class. It is also considered to be an inducer of plant cell elongation and division that can cause uncontrolled growth
Applications
• This compound is a monocarboxylic acid; an acetic acid in which one of the methyl hydrogens has been replaced by a 1H-indol-3-yl group.
• Beyond its role as a plant hormone, this compound regulates tissue differentiation, apical dominance, and responses to light, gravity, and pathogens
• It can be used as a signaling molecule necessary for development of plant organs and coordination of growth
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Fu, S.; Wei, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H.; Chou, J. Indole-3-acetic acid: A widespread physiological code in interactions of fungi with other organisms. Plant Signal Behav. 2015, 10, (8), e1048052.
- Cheryl L. Patten; Bernard R. Glick. Bacterial biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid. Can. J. Microbiol. 1996, 42, (3), 207-220.
- Rigsud, J.; Puppo, A. Indole-3-acetic Acid Catabolism by Soybean Bacteroids. Microbiology. 1975, 88, 223-228.