Search
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
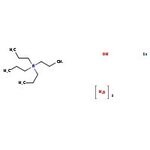
Tetra-n-propylammonium perruthenate(VII), 98%
CAS: 114615-82-6 | C12H35NO4Ru | 358.485 g/mol
化学物質識別子
CAS114615-82-6
IUPAC Nametetrapropylazanium tetrahydrate ruthenium
Molecular FormulaC12H36NO4Ru
InChI KeyHUCLFLGLPCVDMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SMILESO.O.O.O.[Ru].CCC[N+](CCC)(CCC)CCC
さらに表示
Tetra-n-propylammonium perruthenate a catalytic oxidant used in conjunction with N-methylmorpholine N-oxide for oxidation of primary & secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
Tetra-n-propylammonium perruthenate a catalytic oxidant used in conjunction with N-methylmorpholine N-oxide for oxidation of primary & secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones.
Solubility
Insoluble in water.
Notes
Hygroscopic. Store under inert gas. Store away from oxidizing agents, reducing agents, heat, organic materials, metal powders, heat.
Tetra-n-propylammonium perruthenate a catalytic oxidant used in conjunction with N-methylmorpholine N-oxide for oxidation of primary & secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones.
Solubility
Insoluble in water.
Notes
Hygroscopic. Store under inert gas. Store away from oxidizing agents, reducing agents, heat, organic materials, metal powders, heat.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Huan Cheng; Christian B W Stark. A double donor-activated ruthenium(VII) catalyst: synthesis of enantiomerically pure THF-diols. Angewandte Chemie. International edition in English. 2010, 49 (9), 1587-1590.
- Brooks E Maki; Karl A Scheidt. Single-flask synthesis of N-acylated indoles by catalytic dehydrogenative coupling with primary alcohols. Organic Letters. 2009, 11 (7), 1651-1654.
- Selective, catalytic oxidant introduced by Ley. Normally used in combination with N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide as the stoichiometric reoxidant and 4A molecular sieves to remove water. Preferred solvents are dichloromethane and acetonitrile. Primary and secondary alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes and ketones in high yield: J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1625 (1987). For an example of alcohol to aldehyde oxidation in the partial synthesis of the acyl tetronic acid ionophore tetronasin, see: Tetrahedron Lett., 35, 319 (1994). Also useful for a number of other oxidations such as lactols to lactones and sulfides to sulfones. For oxidation of secondary amines to imines, and of hydroxylamines to nitrones, see: Tetrahedron Lett., 35, 6567, 6571 (1994).
- For a comprehensive review of this reagent, see: Synthesis, 639 (1994). For a review of ruthenium oxo-complexes as organic oxidants, see: Chem. Soc. Rev., 21, 179 (1992).
- For a brief feature on uses in synthesis, see: Synlett, 824 (2007).