Search
Thermo Scientific Chemicals
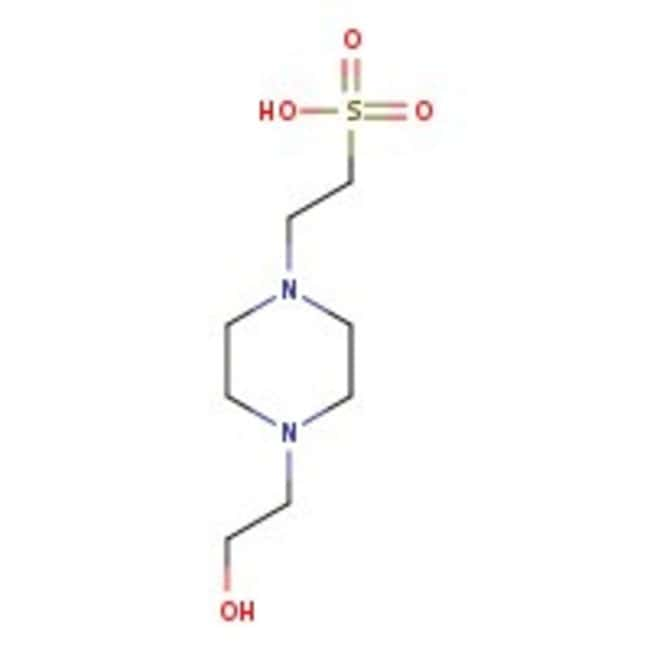
HEPES, 1.0M buffer soln., pH 7.0
CAS: 7365-45-9 | C8H18N2O4S | 238.30 g/mol
化学物質識別子
CAS7365-45-9
IUPAC Name2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethane-1-sulfonic acid
Molecular FormulaC8H18N2O4S
InChI KeyJKMHFZQWWAIEOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SMILESOCCN1CCN(CCS(O)(=O)=O)CC1
さらに表示
仕様 スペックシート
スペックシート
Appearance (Color)Clear colorless
CompositionHEPES: 1 M
CommentComponent is dissolved in UV treated 18.2 megohm-cm ± 1 water, followed by pH adjustment and filtered through 0.22 micron filter.
CompositionSodium Hydroxide: For pH adjustment
pH7.0 ± 0.2
さらに表示
HEPES is common buffer for biological sciences, particularly used in cell culture to maintain physiological pH. It acts a buffering component, which is used in the preparation of buffers. It is described as one of the best all-purpose buffers available for use in biological research.
This Thermo Scientific Chemicals brand product was originally part of the Alfa Aesar product portfolio. Some documentation and label information may refer to the legacy brand. The original Alfa Aesar product / item code or SKU reference has not changed as a part of the brand transition to Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
Applications
HEPES is common buffer for biological sciences, particularly used in cell culture to maintain physiological pH. It acts a buffering component, which is used in the preparation of buffers. It is described as one of the best all-purpose buffers available for use in biological research.
Solubility
Miscible with water.
Notes
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
HEPES is common buffer for biological sciences, particularly used in cell culture to maintain physiological pH. It acts a buffering component, which is used in the preparation of buffers. It is described as one of the best all-purpose buffers available for use in biological research.
Solubility
Miscible with water.
Notes
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
RUO – Research Use Only
General References:
- Johnson, S. E.; Hudson, J. L.; Kapur, J. Synchronization of action potentials during low-magnesium-induced bursting. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 113 (7), 2461-2470.
- Torelli, N. Q.; Ferreira-Júnior, J. R.; Kowaltowski, A. J.; da Cunha, F. M. RTG1-and RTG2-dependent retrograde signaling controls mitochondrial activity and stress resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2015, 81, 30-37.