Search
Citas y referencias (1)
Invitrogen™
Células competentes One Shot™ MAX Efficiency™ DH5α-T1R
Las células competentes One Shot MAX Efficieny DH5α-T1R proceden de la conocida cepa DH5α. DH5α-T1R contiene el genotipo tonA, queMás información
| Número de catálogo | Cantidad |
|---|---|
| 12297016 | 21 x 50 μl |
Número de catálogo 12297016
Precio (CLP)
-
Cantidad:
21 x 50 μl
Las células competentes One Shot MAX Efficieny DH5α-T1R proceden de la conocida cepa DH5α. DH5α-T1R contiene el genotipo tonA, que les confiere resistencia al fago T1 y T5. El bacteriófago T1 se extiende rápidamente y lisa los huéspedes de E. coli, que se suelen emplear para la clonación y la construcción de bibliotecas. Ofrecen una seguridad añadida para proteger clones y bibliotecas de gran valor. Esto es especialmente importante para los centros de secuenciación y genomas, donde la infección de fago T1 sería catastrófica. Además de resistencia a fagos, E. coli DH5α-T1R ofrece las ventajas siguientes:
• Preparaciones de ADN más transparentes y mejores resultados en aplicaciones posteriores debido a la eliminación de la digestión inespecífica por parte de endonucleasa I (endA1)
• Reduce los casos de recombinaciones no deseadas en ADN clonado (recA1)
• Transformación eficaz de ADN no metilado de aplicaciones de PCR (hsdR)
• Detección azul/blanca de clones recombinantes que transportan el fragmento alfa de la β-galactosidasa (lacZΔM15)
Formato práctico y eficaz
E. coli DH5-T1R se suministra en el práctico formato de una sola reacción One Shot. Cada tubo contiene una cantidad suficiente de células para una transformación, sin detrimento de la eficacia ni de los ciclos de congelación y descongelación, además de no desperdiciar dinero en células no utilizadas.
• Preparaciones de ADN más transparentes y mejores resultados en aplicaciones posteriores debido a la eliminación de la digestión inespecífica por parte de endonucleasa I (endA1)
• Reduce los casos de recombinaciones no deseadas en ADN clonado (recA1)
• Transformación eficaz de ADN no metilado de aplicaciones de PCR (hsdR)
• Detección azul/blanca de clones recombinantes que transportan el fragmento alfa de la β-galactosidasa (lacZΔM15)
Formato práctico y eficaz
E. coli DH5-T1R se suministra en el práctico formato de una sola reacción One Shot. Cada tubo contiene una cantidad suficiente de células para una transformación, sin detrimento de la eficacia ni de los ciclos de congelación y descongelación, además de no desperdiciar dinero en células no utilizadas.
Para uso exclusivo en investigación. No apto para uso en procedimientos diagnósticos.
Especificaciones
Resistencia bacteriana a los antibióticosNo
Tramado azul/blancoSí
Clonación de ADN metiladoNo
Clonación de ADN inestableNo es adecuado para clonar ADN inestable
Contiene el episoma F'Carece de episoma F'
Compatibilidad de alto rendimientoNo compatible con alto rendimiento (manual)
Mejora la calidad de los plásmidosSí
Preparación de ADN no metiladoNo es adecuado para preparar ADN no metilado
Línea de productosOne Shot
Tipo de productoCélula competente
Cantidad21 x 50 μl
Reduce la recombinaciónSí
Condiciones de envíoDry Ice
Resistente al fago T1 (tonA)Sí
Nivel de eficiencia de transformaciónAlta eficacia (> 10^9 ufg⁄µ g)
FormatoTubo
EspecieE. coli
Unit SizeEach
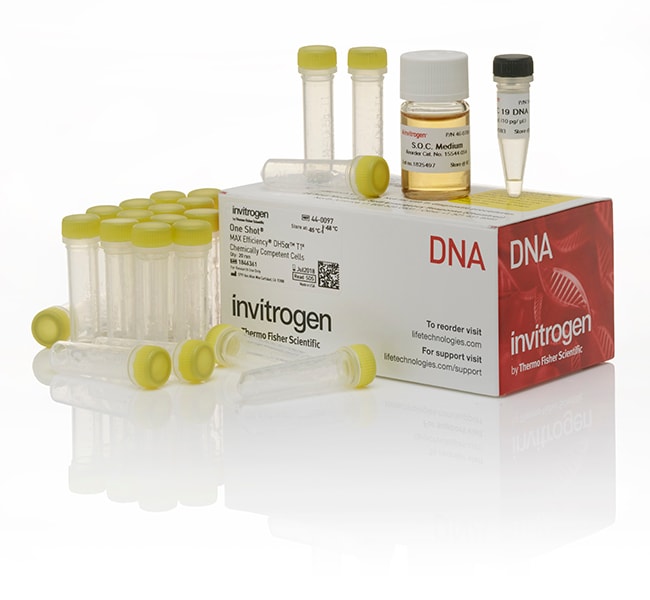
Contenido y almacenamiento
Contiene:
• Células competentes One Shot MAX Efficiency DH5α-T1R: 20 viales, 50 µl cada uno (total de 1 ml)
• ADN pUC19 (10 pg/ul): 1 vial, 50 µl
• Medio S.O.C.: 1 frasco, 6 ml
Almacenar las células competentes a -80 °C. Almacene pUC19 DNA a -20 °C. Almacenar el medio S.O.C. a 4 °C o a temperatura ambiente.
• Células competentes One Shot MAX Efficiency DH5α-T1R: 20 viales, 50 µl cada uno (total de 1 ml)
• ADN pUC19 (10 pg/ul): 1 vial, 50 µl
• Medio S.O.C.: 1 frasco, 6 ml
Almacenar las células competentes a -80 °C. Almacene pUC19 DNA a -20 °C. Almacenar el medio S.O.C. a 4 °C o a temperatura ambiente.
Preguntas frecuentes
How do you recommend that I prepare my DNA for successful electroporation of E. coli?
You offer competent cells in Subcloning Efficiency, Library Efficiency and MAX Efficiency. How do these differ?
Do any Invitrogen competent cells contain DMSO in the freezing medium?
When should DMSO, formamide, glycerol and other cosolvents be used in PCR?
Citations & References (1)
Citations & References
Abstract
Haemophilus influenzae type b strain A2 has multiple sialyltransferases involved in lipooligosaccharide sialylation.
Journal:J Biol Chem
PubMed ID:11842084
The lipooligosaccharide (LOS) of Haemophilus influenzae contains sialylated glycoforms, and a sialyltransferase, Lic3A, has been previously identified. We report evidence for two additional sialyltransferases, SiaA, and LsgB, that affect N-acetyllactosamine containing glycoforms. Mutations in genes we have designated siaA and lsgB affected only the sialylated glycoforms containing N-acetylhexosamine. A mutation