Search Thermo Fisher Scientific
Invitrogen
NFkB p65 Polyclonal Antibody, eBioscience™
This Antibody was verified by Cell treatment to ensure that the antibody binds to the antigen stated.
FIGURE: 1 / 16
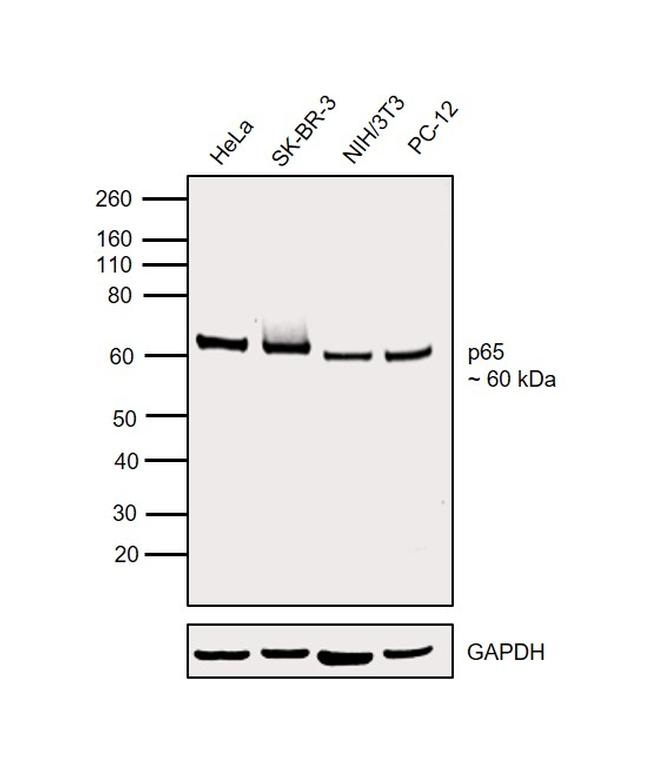
NFkB p65 Antibody (14-6731-81) in WB




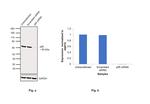

Product Details
14-6731-81
Species Reactivity
Published species
Host/Isotype
Class
Type
Conjugate
Form
Concentration
Purification
Storage buffer
Contains
Storage conditions
Shipping conditions
RRID
Product Specific Information
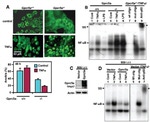
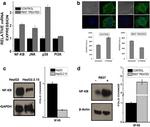
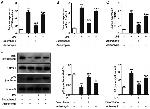
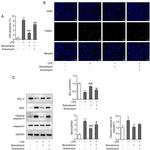
Description: The polyclonal antibody reacts with mouse, rat, and human NFkB p65; the antibody was raised against a peptide mapping to the carboxy terminus of human NFkB p65. Members of the rel/NFkB family of transcription factors are involved in the regulation of cellular responses, such as growth, development, and the inflammatory response. They share a structural motif known as the rel homology region (RHR), the C-terminal one third of which mediates protein dimerization (2, 6, 8). Complexes of p50 (NF-kB1) or p52 (NF-kB2) are generated through the processing of p105 and p100 precursors, respectively. These are usually associated with members of the Rel family (p65, c-Rel, Rel B). The homo- and heterodimer formed through combinations of NFkB/Rel proteins bind distinct kB sites to regulate the transcription of different genes (7, 9). In resting cells, NFkB is retained in the cytoplasm bound to inhibitory proteins of the IkB family. Degradation of IkB proteins occurs with cell activation, via of variety of signals, including inflammatory cytokines and bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) as well as oxidative and fluid mechanical stress. This results in nuclear translocation of NFkB and the transcriptional gene activation of proinflammatory genes (1, 9). It has been suggested that NFkB plays a role in the development of numerous pathological states. Activation of NFkB induces gene programs leading to transcription of factors that promote inflammation, such as leukocyte adhesion molecules, cytokines, and chemokines. It is also thought that there are some substances with possible anti-inflammatory effects that are also NFkB regulated. There is some evidence indicating NFkB as a key factor in the pathophysiology of cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury as well as the development of insulin dependent Diabetes Mellitus (4, 3).
Applications Reported: Purified anti-mo/hu/rat NFkB p65 poly has been reported for use in immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting (WB), and immunohistochemical staining.
Applications Tested: Purified anti-mo/hu/rat NFkB p65 poly has been tested by immunoblotting (WB) and immunohistochemistry. (1:1000 starting dilution). It is recommended that this antibody be titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC.
Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
Target Information
Nuclear factor kB p65 (NF-kB p65) is encoded by the RELA gene and is present on chromosome 11 in humans. NF-kB P65 is also known as RelA (v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A) and belongs to the Rel family of proteins. It is one of the two subunits of NF-kB (Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) that heterodimerizes with the other subunits p50 or p52. However, binding of TNF alpha to its cognate receptor phosphorylates IKK which in turn phosphorylates I kB allowing proteasomal degradation of I kB. It specifically plays a key role in transcription of immunoglobulin k (kappa) gene in mature B-lymphoid cells.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
Bioinformatics
Protein Aliases: avian reticuloendotheliosis viral (v-rel) oncogene homolog A; MGC131774; NF KB; nf-kappa-b p65; NF-kappa-B p65delta3; NF-kappa-B transcription factor p65; NFkappaB p65; nfkb rela; NFkB-p50; NFKB1; nuclear factor; nuclear factor kappa b; nuclear factor kappa B subunit p65; Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 3; p65 NF kappaB; p65 NF-kappa B; p65 NFkB; REL A; Transcription factor p65; v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A; v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A
Gene Aliases: NFkB; NFKB3; p65; RELA
UniProt ID: (Human) Q04206, (Mouse) Q04207
Entrez Gene ID: (Human) 5970, (Mouse) 19697, (Rat) 309165
Molecular Function:
![]() Rel homology transcription factor
Rel homology transcription factor

Performance Guarantee
If an Invitrogen™ antibody doesn't perform as described on our website or datasheet,we'll replace the product at no cost to you, or provide you with a credit for a future purchase.*
Learn more
We're here to help
Get expert recommendations for common problems or connect directly with an on staff expert for technical assistance related to applications, equipment and general product use.
Contact tech support