Search
Oncomine Dx Target Test Technical and Validation Information

Established performance
The Ion Torrent Oncomine Dx Target Test is the first targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) in vitro diagnostic test simultaneously delivering multiple biomarker results to aid selection of targeted therapies for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), cholangiocarcinoma (CC), anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC), astrocytoma (AC), oligodendroglioma (OG), medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), and thyroid cancer (TC) patients. Concordance with FDA-approved or validated reference methods based on fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), polymerase chain reaction (PCR), Sanger sequencing, or NGS was established for all CDx biomarkers included in the test. The variants for KRAS, MET and PIK3CA have been analytically validated. Performance of all other variants identified by the test, other than the clinically validated therapeutic variants and analytically validated variants, has not been directly demonstrated.
Oncomine Dx Target Test content
Gene targets included for NSCLC
| Gene targets for therapeutic use | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRAF: V600E | EGFR: L858R, exon 19 deletions, and exon 20 insertions | ERBB2/HER2: activating mutations (SNVs and exon 20 insertions) | ERBB2/HER2: activating mutations (SNVs in exons 18–21 within the tyrosine kinase domain and exon 20 insertions) | RET: fusions | ROS1: fusions |
| Analytically validated targets | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KRAS | MET* | PIK3CA | ||||
| Additional targets** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | HRAS | MTOR | RET | ROS1 |
| ALK* | ERBB3 | KIT | NRAS | |
| CDK4 | FGFR2 | MAP2K1 | PDGFRA | |
| DDR2 | FGFR3 | MAP2K2 | RAF1 | |
Figure 1. Complete gene list. *The test reports fusion/translocation variants for ROS1 and RET only. This test only reports mutations for ALK and MET. ** Performance for the additional gene target variants has been validated based on a representative method. Only IDH1 is reported for CC. Only RET mutations are reported for MTC and only RET fusions are reported for TC.
Performance characteristics
Select analytical and clinical studies are summarized below. For complete studies and results, refer to the Oncomine Dx Target Test Part I: Test Description and Performance Characteristics User Guide
Limit of detection
The LoD was evaluated for 5 IDH1 R132 variants detected by the Oncomine Dx Target Test. The LoD is the lowest allelic frequency (AF) that can be detected at least 95% of the time. The study demonstrated LoD of the 5 IDH1 R132 variants ranged from 4.5–5.7% AF, including 4.5% AF for R132C, 5.7% AF for R132G, 4.9% AF for R132H, 5.1% AF for R132L, and 5.3% AF for R132S.
Assay reproducibility
The reproducibility and repeatability of IDH1 R132 variant detection using Oncomine Dx Target Test were assessed with 1 IDH1 WT sample and three IDH1 R132 variant-positive samples at 2 allele frequency levels. Testing was performed at 4 testing sites using 4 lots of reagents, and each site had 2 PGM Dx instrument systems and 2 operators. The overall positive call rate for IDH1 R132 variants was 92.6% when including no calls and 97.1% when excluding no calls. The negative call rate for IDH1 WT sample were 100% at all IDH1 R132 variant locations (Table 1).
Table 1. Reproducibility results for IDH1 in cholangiocarcinoma
Sample
|
Variant ID
| Positive call rate +95% Cl | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Variant (amino acid change) | # of valid sample results (N) | # of positive calls (A) | # of positive calls (B) | # of positive calls (C) | Including no calls (A/N) | Excluding no calls (A/(A+B)) | Relative LoD | ||
D1 | COSM28747 | R132C | 36 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 100% (90.3%, 100%) | 100% (90.3%, 100%) | 2.1–2.7X |
D2 | COSM28747 | R132C | 36 | 35 | 0 | 1 | 97.2% (85.5%, 99.9%) | 100% (90.0%, 100%) | 0.98–1.4X |
D3 | COSM28749 | R132G | 36 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 100% (90.3%, 100%) | 100% (90.3%, 100%) | 1.9–2.5X |
D4 | COSM28749 | R132G | 36 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 100% (90.3%, 100%) | 100% (90.3%, 100%) | 0.9–1.3X |
D5 | COSM28750 | R132L | 36 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 100% (90.3%, 100%) | 100% (90.3%, 100%) | 1.4–1.8X |
D6 | COSM28750 | R132L | 35 | 20 | 6 | 9[1] | 57.1% (39.4%, 73.7%) | 76.9% (56.4%, 91.0%) | 0.65–0.94X |
D7 | Wild-type (WT) | N/A | 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0% (0%, 9.17%) | 0% (90.3%, 100%) | N/A |
Condordance
A clinical concordance study was conducted to evaluate the ability of the Oncomine Dx Target Test to identify 5 IDH1 biomarkers in FFPE cholangiocarcinoma tumor specimen compared to a validated Sanger assay. The study demonstrated OPA of 97.9%, excluding invalids and no calls. A summary of the data is included in Table 2.
Table 2. Concordance results for IDH1
Agreement measure | Excluding invalid and no calls | Including invalid results and no-calls | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Percent agreement | 95% Cl | Percent agreement | 95% Cl | |
| PPA | 99.4% (163/164) | (96.7%, 100.0%) | 97.0% (163/168) | (93.2%, 99.0%) |
| NPA | 96.5% (164/170) | (92.5%, 98.7%) | 90.6% (164/181) | (85.4%, 94.4%) |
| OPA | 97.9% (327/334) | (95.7%, 99.2%) | 93.7% (327/349) | (90.6%, 96.0%) |
Limit of detection
The LoD of the Oncomine™ Dx Target Test for 10 IDH1 and IDH2 SNVs was determined using various FFPE clinical samples and DNA sample blends across 6 dilution levels. The LoD for the 5 IDH1 SNVs ranged from 4.6% to 7.0% AF, while the LoD for the 5 IDH2 SNVs ranged from 4.1% to 5.8% AF.
Assay reproducibility
The reproducibility and repeatability of detecting IDH1 and IDH2 variants in astrocytoma and oligodendroglioma samples were assessed across three test sites. The study involved 12 positive sample blends and one negative blend, tested by 2 operators per site using 2 Ion PGM Dx systems and 3 reagent lots. Each operator performed 12 replicates per sample blend, resulting in a total of 156 valid sequencing runs. The overall positive call rate for IDH1 variants was 100%, and for IDH2 variants, it was 97.5% including no calls and 99.9% excluding no calls. The negative call rate and within-run repeatability for IDH1 variants were both 100%, while IDH2 repeatability ranged from 95.8% to 100% excluding no calls.
Concordance
A clinical concordance study was to evaluate the concordance between the Oncomine Dx Target Test and local laboratory tests (LLT) for IDH1/IDH2 mutations in glioma specimens. A summary of the results is detailed in Tables 3 and 4.
Table 3. Concordance between Oncomine Dx Target Test and NGS LLT assay for IDH1/IDH2 mutation
Oncomine Dx Target Test (IDH1/IDH2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
NGS LLT assay (IDH1/IDH2) | ||||
Frequency | Positive | Negative | Unknown | Total |
| Positive | 306 | 0 | 21 | 327 |
| Negative | 1 | 34 | 1 | 36 |
| Unknown | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Total | 307 | 37 | 22 | 366 |
Table 4. Clinical concordance of the Oncomine™ Dx Target Test in reference to NGS LLT assay for IDH1/IDH2 mutation
Agreement measure | Estimate | 95% Cl |
|---|---|---|
| PPA | 99.7% | (98.2%, 99.9%) |
| NPA | 100% | (89.8%,100.0%) |
| Adjusted PPV | 100% | (98.8%, 100.0%) |
| Adjusted NPV | 100% | (89.8%, 100.0%) |
Limit of detection
The LoD of the Oncomine Dx Target Test was evaluated across several studies to determine the lowest AF that can be detected at least 95% of the time.
- Study I: The LoD for 14 representative DNA variants representing 3 variant categories (SNV, multi-nucleotide polymorphism (MNP), or deletion variants) were determined to 6–8% AF.
- Study II: The LoD for ROS1 fusion detection using RNA from fusion-positive clinical FFPE specimens was determined to be 516 fusion reads.
- Study III: The LoD for RET fusion detection using RNA from fusion-positive clinical FFPE specimens was determined to be 405 fusion reads.
- Study IV: The LoD for EGFR exon 20 insertion detection was determined to be 4.8–5.2% AF.
- Study V: The LoD for ERBB2/HER2 exon 20 insertion detection was determined to be 4.8–5.0% AF.
- Study VI: The LoD for ERBB2/HER2 SNV detection was determined to be 4.5–5.8% AF.
- Study VII: The LoD for EGFR exon 20 insertion variants (3 bp and 12 bp) was determined to be 6.48% AF for the 3 bp insertion and 5.54% AF for the 12 bp insertion.
- Study VIII: The LoD results for 3 EGFR exon 20 insertion variants (3 bp, 9 bp, and 12 bp) were confirmed using DNA from insertion-positive clinical FFPE specimens blended with WT DNA to target 1X–1.5X LoD. The study confirmed the established LoD estimates, with slight variations in AF for specific variants.
Panel accuracy
To evaluate the ability of the Oncomine Dx Target Test DNA and RNA panels to identify somatic variants in human specimens, 290 FFPE tumor samples were analyzed using the Oncomine™ Dx Target Test to demonstrate positive percent agreement (PPA) and negative percent agreement (NPA) concordance with validated reference detection methods including:
- A validated NGS assay, to detect SNV and deletion hotspot variants
- A ROS1 FISH reference test, to detect ROS1 fusions
- A RET FISH reference test, to detect RET fusions
The study demonstrated variant level PPA of 98.5%, NPA of 100%, and OPA of 100%, excluding invalids no-calls; and PPA level of 98.5%, NPA of 96.8%, and OPA of 96.8% including no-calls. A summary of the data is included in Table 5. For details see the User Manual.
Table 5. Variant level accuracy study results
Variant level measure of agreement | Percent agreement (N) | Percent agreement (N) |
|---|---|---|
Positive percent agreement | 98.5% (195/198) | 98.5% (195/198) |
Negative percent agreement | 100.0% (118,155/118,159) | 96.8% (118,155/122,012) |
Overall percent agreement | 100.0% (118,350/118,357) | 96.8% (118,350/122,210) |
Reproducibility
The reproducibility and repeatability were validated across multiple studies for various DNA and RNA variants, including SNVs, deletions, and fusions.
Study I:
Reproducibility and repeatability were evaluated using 30 representative variants from 18 DNA samples. The study was designed to evaluate within-run precision performance (repeatability) and variability across sites, operators, and instruments (reproducibility). Due to the large number of variants detected by the test and the rarity of some of the variants, a representative variant approach was used. Variants were selected in the following categories:
- Simple SNVs
- Complex SNVs and MNPs, including SNVs in di- or tri-nucleotide repeat regions and SNVs in high-GC (>60%) or low-GC (<40%) content regions
- Deletions (including deletions of 6, 9, 15, and 18 bp)
The study demonstrated a call rate of >96% excluding no calls, and the estimate of repeatability was >98.8%, excluding no calls.
Study II:
Study II assessed reproducibility and repeatability for 6 representative variants from 11 DNA and 4 RNA clinical samples across multiple sites, operators, and instruments. The call rate for variant-positive DNA was 99%, while WT DNA had a call rate of 100%, excluding no calls. For ROS1 fusion-positive RNA, the call rate was 100%, and WT RNA had a call rate of 99%, excluding no calls.
Study III:
The reproducibility and repeatability for detecting RET fusions were evaluated using 4 RET fusion-positive and 2 RET fusion-negative RNA samples. The study showed a call rate of 99% for RET fusion-positive RNA and 100% for WT RNA, excluding no calls.
Study IV:
Reproducibility and repeatability for detecting EGFR exon 20 insertion variants were assessed using 2 EGFR variant-positive and 2 EGFR variant-negative DNA samples. The call rate for EGFR exon 20 insertion-positive DNA was 100%, and WT DNA had a call rate of 100%, excluding no calls.
Study V:
Reproducibility and repeatability for detecting ERBB2/HER2 exon 20 insertion variants was evaluated using 2 ERBB2/HER2 variant-positive and 2 ERBB2/HER2 variant-negative DNA samples. The call rate for ERBB2/HER2 exon 20 insertion-positive DNA was 100%, and WT DNA had a call rate of 100%, excluding no calls.
Study VI:
Reproducibility and repeatability for detecting ERBB2/HER2 SNVs were evaluated using 3 ERBB2/HER2 SNV-positive and 4 ERBB2/HER2 SNV-negative DNA samples. The call rate for ERBB2/HER2 SNV-positive DNA was 100%, and WT DNA had a call rate of 100%, excluding no calls.
Study VII:
Reproducibility and repeatability for detecting RET fusions near the LoD were evaluated using 4 RET fusion-positive and 2 WT RNA samples. The study demonstrated positive call rates of 77.8% for the KIF5B-RET fusion isoform and 100% for the CCDC6-RET fusion isoform, excluding no calls.
Study VIII:
Reproducibility and repeatability for the KIF5B-RET fusion at 1X LoD was confirmed with a call rate 94.4% for the KIF5B-RET fusion isoform, excluding no calls.
Study IX:
Reproducibility and repeatability for 3 EGFR exon 20 insertion variants (3 bp, 9 bp, and 12 bp) was confirmed with a call rate of 100% for EGFR exon 20 insertion-positive DNA variants, excluding no calls
The accuracy of the Oncomine Dx Target Test for detecting various biomarkers in NSCLC was evaluated with method comparison studies against several reference assays including PCR, NGS, and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). A summary of the results is shown below. For details, refer to the Oncomine Dx Target Test Part I: Test Description and Performance Characteristics User Guide.
Table 6. Concordance of the Oncomine Dx Target Test with various reference assays
Variants for therapy selection
|
Validated comparator methods
| Excluding no calls or unknowns* | Including no calls or unknowns* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Positive percent agreement | Negative percent agreement | Overall percent agreement | Positive percent agreement | Negative percent agreement | Overall percent agreement | ||
BRAF V600E | BRAF V600E qPCR test | 100% (67/67) | 100% (114/114) | 100% (181/181) | 91.8% (67/73) | 97.4% (114/117) | 95.3% (181/190) |
EGFR | therascreen™ EGFR PCR Kit | 98.6% (71/72) | 99.2% (120/121) | 99.0% (191/193) | 81.6% (71/87) | 96.8% (120/124) | 90.5% (191/211) |
EGFR exon 19 deletions | 97.6% (41/42) | 99.3% (147/148) | 99.0% (188/190) | 74.6% (41/55) | 94.2% (147/156) | 89.1% (188/211) | |
EGFR exon 21 L858R | 100% (30/30) | 100% (167/167) | 100% (197/197) | 93.8% (30/32) | 93.3% (167/179) | 93.4% (197/211) | |
| EGFR exon 20 insertions | NGS assay 1 | 100% (54/54) | 100% (95/95) | 100% (149/149) | 98.2% (54/55) | 90.5% (95/105) | 93.1% (149/160) |
| NGS Assay 2 | 100% (46/46) | 100% (63/63) | 100% (109/109) | 97.9% (46/47) | 91.3% (63/69) | 94.0% (109/116) | |
| ERBB2/HER2 activating mutations (SNVs and exon 20 insertions) | LLT | 100% (38/38) | 99.1% (108/109) | 99.3% (146/147) | 97.4% (38/39) | 92.3% (108/117) | 93.6% (146/156) |
| ERBB2/HER2 activating mutations (SNVs in exons 18–21 within the tyrosine kinase domain and exon 20 insertions) | LLT | 94.7% (72/76) | 100% (130/130) | 98.1% (202/206) | 56.3% (72/128 | 95.6% (130/136) | 76.5% (202/264) |
| LLT | 100% (76/76) | 100% (125/125) | 100% (201/201) | 92.7% (76/82) | 92.6% (125/135) | 92.6% (201/217) | |
ROS1 fusions | ROS1 FISH test | 100% (9/9) | 100% | 100% | 90.0% (9/10) | 88.6% (62/70) | 88.8% (71/80) |
| RET fusions | NGS Assay 1 | 90.9% (40/44) | 91.8% (101/110) | 91.6% (141/154) | 90.9% (40/44) | 91.8% (101/110) | 91.6% (141/154) |
| NGS Assay 2 | 92.3% (84/91) | 96.8% (121/125) | 94.9% (205/216) | 92.3% (84/91) | 96.0% (121/126) | 94.5% (205/217) | |
* Unknowns are defined as values due to insufficient sample, failed pathology review, or sample QC sequencing failure resulting in an invalid result or No Call for the variant.
** EGFR exon 19 deletions and exon 21 L858R combined.
† Local laboratory test/Clinical trial assay
Limit of detection
The LoD of the Oncomine Dx Target Test for detection of BRAF V600E mutation in thyroid cancer FFPE tissue was 6.4% AF, which confirmed the established LoD for BRAF V600E in NSCLC tissues.
Reproducibility
Reproducibility and repeatability for BRAF V600E was evaluated with two variant-positive and one variant-negative thyroid cancer sample. The results demonstrated 100% agreement for average positive and average negative agreements (APA, ANA), across all replicates, operators, instruments, and reagent lots.
Concordance of the Oncomine Dx Target Test with a clinical trial PCR assay in the detection of BRAF V600E variants in ATC was evaluated using 199 samples, which included 32 from the ATC clinical trial and 167 commercially sourced thyroid cancer tissue samples of various histologies including follicular (FTC), papillary (PTC), and medullary thyroid cancer (MTC). The PPA, NPA, and overall percent agreement (OPA) results are shown in Table 7.
Table 7. Concordance between the clinical trial PCR assay and the Oncomine Dx Target Test
Agreement measure | Excluding invalid and no calls | Including invalid results and no-calls | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Percent agreement | 95% Cl1 | Percent agreement | 95% Cl1 | |
| PPA | 99.0% (97/98) | (94.4%, 99.8%) | 77.6% (97/125) | (69.5%, 84.0%) |
| NPA | 100% (57/57) | (93.7%, 100.0%) | 77.0% (57/74) | (66.3%, 85.1%) |
| OPA | 99.4% (154/155) | (96.4%, 99.9%) | 77.4% (154/199) | (71.1%, 82.6%) |
1The 95% Cl was calculated using the Wilson Score method.
Limit of detection
The LoD for the Oncomine Dx Target Test was evaluated for 4 RET DNA variants and 2 RET RNA fusions in clinical thyroid cancer samples. The LoD for RET DNA variants were determined to be allelic frequencies ranging from 4.9% to 5.5% AF, and the LoD for RET RNA fusions was 236 fusion reads.
Reproducibility
Reproducibility and repeatability were evaluated for detection of RET DNA variants and RET RNA fusions. The call rate for RET variant-positive DNA was 100%, and WT DNA had a call rate of 100%, excluding no calls. The call rate was 97.4% for RET fusion-positive RNA, and 100% for WT RNA. Estimates of within-run repeatability were 100% for the RET DNA variants tested, with one WT blend showing a 97.9% repeatability with no calls included. Repeatability estimates for the RET RNA fusion blends tested ranged from 88.9% to 100%.
Concordance was evaluated for detecting RET DNA variants and fusions in medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) and other thyroid cancer (TC) specimens through various method comparison studies comparing to validated reference NGS assays and local laboratory tests (LLTs). The concordance of RET DNA variants and RET fusions are shown in Tables 8-10 below.
Table 8. Concordance between Oncomine Dx Target Test and the reference assay—RET DNA variants (MTC)
Agreement measure | Excluding unknowns1 | Including unknowns1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Percent agreement | 95% Cl | Percent agreement | 95% Cl | |
| PPA | 100.0% (36/36) | (90.3%, 100.0%) | 100.0% (36/36) | (90.3%, 100.0%) |
| NPA | 98.3% (57/58) | (90.8%, 100.0%) | 86.4% (57/66) | (75.7%, 93.6%) |
| OPA | 98.9% (93/94) | (94.2%, 100.0%) | 91.2% (93/102) | (83.9%, 95.9%) |
1Unknowns are defined as invalid or no result using the Oncomine Dx Target Test.
Table 9. Concordance between Oncomine™ Dx Target Test and the reference assay—RET fusions (TC)
Agreement measure | Excluding unknowns1 | Including unknowns1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Percent agreement | 95% Cl | Percent agreement | 95% Cl | |
| PPA | 100.0% (25/25) | (86.3%, 100.0%) | 100.0% (25/25) | (86.3%, 100.0%) |
| NPA | 100.0% (57/57) | (93.7%, 100.0%) | 91.9% (57/62) | (82.2%, 97.3%) |
| OPA | 100.0% (82/82) | (95.6%, 100.0%) | 94.3% (82/87) | (87.1%, 98.1%) |
1Unknowns are defined as invalid or no result using the Oncomine Dx Target Test.
Table 10. Concordance between Oncomine™ Dx Target Test and LLT—RET fusions (TC)
Agreement measure | Excluding unknowns1 | Including unknowns1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Percent agreement | 95% Cl | Percent agreement | 95% Cl | |
| PPA | 93.33% (42/45) | (81.73%, 98.60%) | 64.62% (42/65) | (51.77%, 76.08%) |
| NPA | 100.0% (133/133) | (97.26%, 100.0%) | 87.5% (133/152) | (81.17%, 92.30%) |
| OPA | 98.31% (175/178) | (95.15%, 99.65%) | 80.65% (175/217) | (74.75%, 85.68%) |
1Unknowns are defined as invalid or no result using the Oncomine Dx Target Test.
A complete and flexible system
The Oncomine Dx Target Test is used in conjunction with the Ion PGM Dx System, which includes a complete NGS system of instruments, reagents, and software. The Ion PGM Dx System was initially validated using challenging germline variants and is now additionally validated with the Oncomine Dx Target Test for somatic mutation reporting for FFPE tissue samples. The Ion PGM Dx sequencing system is a Class II 510 K Medical Device and incorporates combined functionality, with both "IVD Mode" for molecular diagnostic tests and "Assay Development Mode" for clinical research. The system also facilitates 21CFR Part 11 compliance, role-based workflows, sample and reagent tracking, QC metrics, and audit trails.
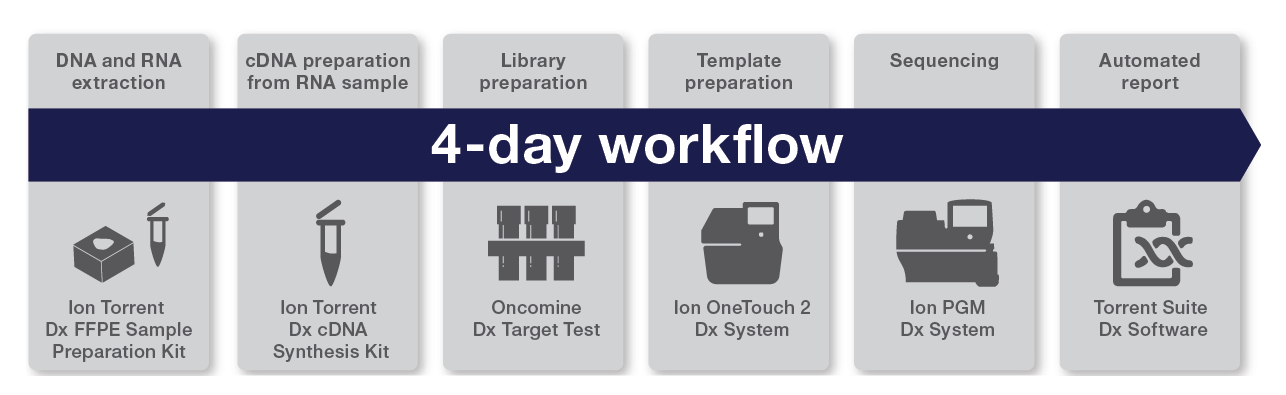
The Oncomine Dx Target Test workflow—all results in 4 days
The Oncomine Dx Target Test workflow is a fully validated IVD workflow from beginning to end and includes all the reagents, consumables, instruments, and software to perform the test. It is possible to run 1–6 samples per run, plus 2 controls within 4 days (Figure 2).
Abbreviated Intended Use: The Oncomine Dx Target Test is a qualitative in vitro diagnostic test that uses targeted high-throughput, parallel-sequencing technology to detect single nucleotide variants (SNVs), deletions, and insertions in 23 genes from DNA and fusions in ROS1 and RET from RNA isolated from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded(FFPE) tumor tissue samples from patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), IDH1 SNVs from FFPE tumor tissue samples from patients with cholangiocarcinoma (CC), BRAF V600E mutations from FFPE tumor tissue samples from patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC), IDH1 and IDH2 SNVs from FFPE tumor tissue samples from patients with astrocytoma (AC) or oligodendroglioma (OG), RET SNVs, multi-nucleotide variants (MNVs), and deletions from DNA isolated from FFPE tumor tissue samples from patients with medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), and RET fusions from RNA isolated from FFPE tumor tissue samples from patients with thyroid cancer (TC) using the Ion PGM™ Dx System.
- Use of this product must be limited to personnel trained in the techniques of PCR, NGS, and the use of the Oncomine Dx Target Test and the Ion PGM Dx System.
- The Oncomine Dx Target Test has only been validated for use with FFPE tumor slide specimens. The use of fine needle aspirates for thyroid cancer (TC) specimens has not been validated.
- The Oncomine Dx Target Test has been validated to detect the following somatic mutations: single-nucleotide variations (SNVs), multinucleotide variations (MNVs), deletions of 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and 18 base pairs, and insertions of 3, 6, 9, and 12 base pairs in DNA, and fusions in RNA.
- The Oncomine Dx Target Test is only validated for use with the Ion PGM Dx System and the Veriti Dx 96‑well Thermal Cycler, 0.2 mL.
- The Oncomine Dx Target Test is only validated for use with 10 ng each of DNA and RNA per sample. Input amounts less than or greater than 10 ng are not recommended.
- Both the DNA and RNA from a single sample extraction must meet the concentration requirements specified in the procedure. Do not use DNA from one extraction with RNA from a different extraction.
- The effects of potential variations in FFPE specimen fixation have not been evaluated.
- Extraction from FFPE sample curls has not been evaluated.
- A potential source of contamination in the procedure is nucleic acid from previous sample processing steps. Follow good laboratory practices and all precautions and guidelines in these user guides to avoid cross-contamination between samples.
- The Oncomine Dx Target Test is a qualitative test. The test is not for quantitative measurements of percent mutation.
- Interference in variant calling can be observed at higher concentrations of chenodeoxycholic acid (≥30 nmol/mL bile acid) in cholangiocarcinoma (CC) clinical FFPE samples with IDH1 variants present at an allelic frequency near the limit of detection (LoD).
- The Oncomine Dx Target Test has not been validated for the detection of RET insertions.
- Users are cautioned that DNA variant-positive calls in the RET genomic region have been observed to produce multiple variant calls, even when only one variant is present. These RET variants are all activating and do not change the patient’s clinical appropriateness for selpercatinib.
- High variation in fusion reads can be observed with fusion-positive samples. A decrease in fusion reads over time has been observed when testing slides from TC tissue under storage.
- For non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the Oncomine Dx Target Test assay definition file includes prevalent but not all rare or newly identified RET isoforms, ROS1 isoforms, EGFR exon 20insertions, EGFR exon 19 deletions, and ERBB2/HER2 activating mutations. The Oncomine Dx Target Test may miss rare, complex, or newly identified:
- RET isoforms carried by a subset of patients who may derive benefit from pralsetinib or selpercatinib
- ROS1 isoforms carried by a subset of patients who may derive benefit from crizotinib
- EGFR exon 20 insertions carried by a subset of patients who may derive benefit from amivantamab-vmjw
- EGFR exon 19 deletions carried by a subset of patients who may derive benefit from gefitinib
- ERBB2/HER2 activating mutations carried by a subset of patients who may derive benefit from fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki
- For TC, the Oncomine Dx Target Test assay definition file includes the most prevalent but not all rare or newly identified RET isoforms. The Oncomine Dx Target Test may miss a subset of patients carrying these rare or newly identified RET isoforms who may derive benefit from selpercatinib.
- For medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), the Oncomine Dx Target Test assay definition file includes the most prevalent but not all rare or newly identified RET SNVs, MNVs and deletions. The Oncomine Dx Target Test may miss a subset of patients carrying these rare or newly identified RET SNVs, MNVs and deletions who may derive benefit from selpercatinib.
- For astrocytoma (AC) and oligodendroglioma (OG), the Oncomine Dx Target Test included prevalent but not all rare IDH2 variant clinical specimens in the assay reproducibility study. The Oncomine Dx Target Test may miss rare IDH2 variants carried by patients who may derive benefit from vorasidenib.
- The Oncomine Dx Target Test has only been validated for use with FFPE tumor slide specimens. The validation of the use of derivative core needle biopsy (CNB) samples and stereotactic biopsy (STB) samples for astrocytoma (AC) and oligodendroglioma (OG), with the Oncomine™ Dx Target Test to support inclusion of these type of samples has not been performed.
- The safe and effective use of the variants reported in Table 2has not been established for selecting therapy using this device. The variants for KRAS (COSM512/p.Gly12Phe/c.34_35delGGinsTT and COSM516/p.Gly12Cys/ c.34G>T), MET (COSM707/p.Thr1010Ile/c.3029C>T) and PIK3CA (COSM754/p.Asn345Lys/c.1035T>A) have been analytically validated. Performance of all other variants identified by the test, other than the clinically validated therapeutic variants and analytically validated variants, has not been directly demonstrated.
For In Vitro Diagnostic Use