Search
SYTOX Green Nucleic Acid Stain Protocol

Dead cell indicator for microscopy
SYTOX Green Nucleic Acid Stain is a bright, high-affinity nucleic acid stain that easily penetrates cells with compromised plasma membranes but does not cross the membranes of live cells, making it a useful indicator of dead cells within a population.
This protocol can be used for:
- Nucleic acid (nuclear) staining in fluorescence microscopy
This protocol should not be used for:
- Flow cytometry
You will need the following for this protocol:
- Cells growing in culture
- SYTOX Green Nucleic Acid Stain (Cat. No. S7020)
- Phosphate-free buffer
- Fluorescence microscope
Protocol
Labeling fixed cells
First, fix and permeabilize cultured cells with a protocol appropriate for your sample.
|
Spectral information and storage
| SYTOX Green | |
|---|---|
| Excitation/Emission (nm) | 504/523 |
| Standard filter set | GFP |
| EVOS Light Cube | GFP |
| Storage conditions | ≤–20°C |
Protocol tips
- Warm to room temperature and briefly centrifuge the DMSO solution to the bottom of the vial each time before use.
- Try multiple dye concentrations in the range from 10 nM to 1 µM to determine the optimal concentration.
- In general, the best results are obtained in buffers that do not contain phosphate, such as Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (Cat. No. 14025-092).
- Treat all nucleic acid binding dyes as potential mutagens and handle with care.
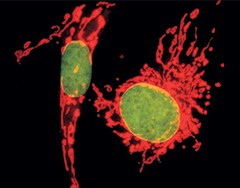
Multicolor staining of BPAECs. Mitochondria of BPAECs were stained with MitoTracker Red CM-H2XRos. The cells were then fixed, permeabilized, RNase-treated, stained with SYTOX Green Nucleic Acid Stain, and imaged.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.